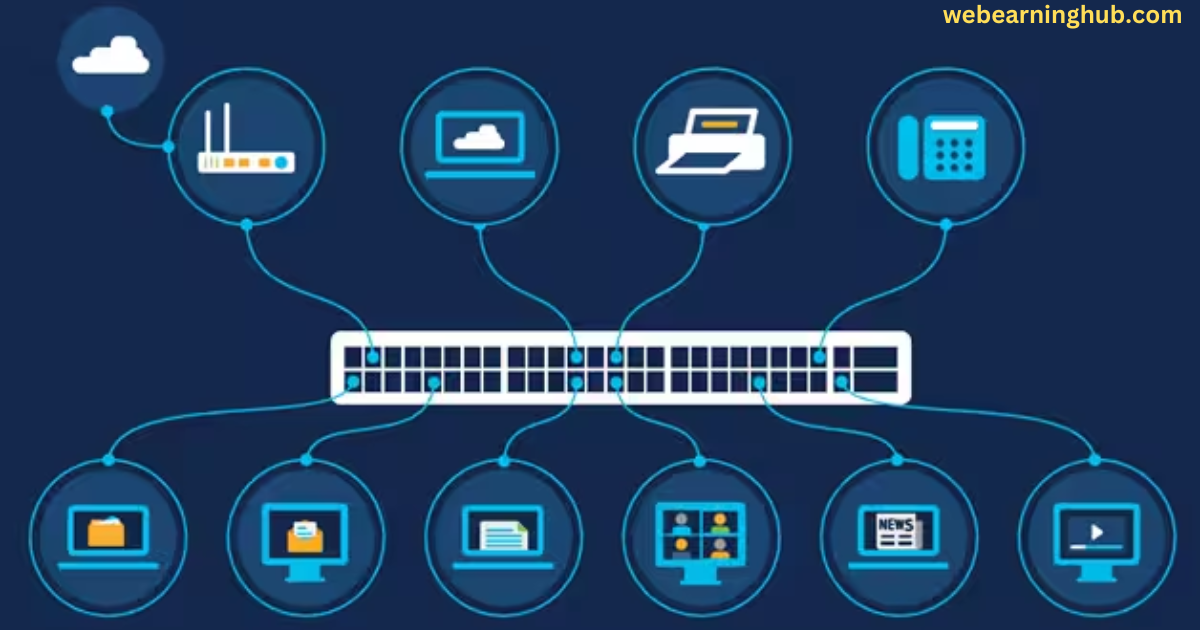
Local Area Network is a small area network that consist of some computers which are associated with each other with the help of networking medium and also some other nodes are connected in the network such as printer, scanner etc. Here we are going to study some basics of Local Area Network.
IEEE Standards-
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers) is worlds largest technical professional association that promotes engineering and electronic improvement for the benefit of humanity. The IEEE 802 standard is for Local Area Network, Metropolitan Area Network and other area network. The IEEE 802 was started in February 1980. The IEEE 802 committee defines frames, speed, distance and types of cabling to use for networking.
Protocols-
In a network there is some procedure that have to follow for data transmission and they are called as protocols. Protocols are set of rules which are used by the nodes on a network to communicate with each other. Protocols are developed by the committees, different companies and than develop or produce products confirming to those protocols. There some standard protocols of network, which are as follows-
- Ethernet Protocol
- Token Ring Protocol
- ARC net Protocol
IEEE 802/LAN/Ethernet Architecture-
- IEEE 802.3
IEEE 802.3 defines a standard Physical Layer and Data Link Layer of Ethernet architecture that uses wired connection. Ethernet is an architecture that mainly uses BUS topology. IEEE 802.3 defines various cabling that used for different types of topologies.
- IEEE 802.4
IEEE 802.4 defines a standard for Token BUS architecture. Token BUS is similar to Token Ring, but it uses coaxial cables.
- IEEE 802.5
IEEE 802.5 defines a standard for Token Ring architecture. IEEE 802.5 uses 10baseT cabling standard. This architecture uses twisted pair cabling to connect devices instead of coaxial cable. It passes data from one computer to another computer like in a Token BUS network does.
Logical Relationship Of IEEE 802.3 With OSI Reference Model-
Like OSI model of networking the IEEE 802.3 also have layers to communicate on the network. The Physical Layer of the IEEE 802.3 standard is corresponds to the Physical Layer of the OSI model. The Data Link Layer of OSI model is divided into two layers in IEEE 802.3 standard, which are called as Logical Link Control Layer (LLC) and Media Access Control (MAC).
| OSI Model | IEEE 802.3 |
| Application Layer | Upper Layer Protocols |
| Presentation Layer | |
| Session Layer | |
| Transport Layer | |
| Network Layer | |
| Data Link Layer | Logical Link Control |
| Media Access Control | |
| Physical Layer | Physical Layer |
IEEE Defines Ethernet-
As defined by the IEEE the Ethernet standard is 802.3 and this standard is mostly adopted for LAN technology. IEEE 802.3 supports data transfer rates of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps and 1 GBps. There are three data rate currently define for the operation over Optical Fiber and Twisted Pair cables.
10 Mbps – 10 Base T Ethernet
100 Mbps – Fast Ethernet
1000 Mbps – Gigabit Ethernet
Working Of Ethernet Network-
In this network system Ethernet frame is used to transfer data over a network. Each frame defines a Ethernet network is uniquely identified a 48 bit (6 byte) address called Ethernet address. Ethernet address are represented as six pairs of hexadecimal digits separated by a colon.
| Elements of Ethernet System | ||
| Medium | Set of Media Access Control Rules | Ethernet Frame |
Ethernet Medium-
Ethernet medium transmits information over the network. Suppose there is a set of computer A, B and D and a printer C. So, if computer D transmits information for printer C, computer B and A also receives the information. All devices connected in this network inspects the destination address. If the received frame in not meant for them, they will reject the frame.
Data Transmission-
When a computer wants to transmit data on the network, it listens to the cable. If two or more devices simultaneously transmit data on an idle cable, collision occurs. Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) permits one device to access to the network media at a time to avoid collision.
Networks that are using CSMA/CD technology such as Ethernet network, the devices connected in the network should compete for the network media. Carrier Sensing Multiple Access / Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) which is a set of rules that can avoid collision, unlike CSMA/CD that handles network transmission, once collision are detected in CSMA/CD, all devices are forced to wait for a random number of time slots and sense the medium. The medium is sensed to be busy, the device stops the timer until it becomes free again.
Types Of Ethernet (Cabling Standards)-
10 Base 5–
Thick Coaxial cable is used in this network type, so it is also referred to as Thicknet. 10 Base 5 refers to specifications of thick coaxial cable carrying Ethernet signals. The 5 is refers to maximum segment length being 500 meters. RG-8 coaxial cable is used in the network. A 15 pin female DB connector, called AUI connector, is used to connect the device.
10 Base 2-
Thin coaxial cable is used in the 10 Base 2 network. So, it is also referred as Thinnet. In 10 Base 2, “2” refers to approximate maximum segment length of the cable which is 185 meters. 10 Base 2 uses RG 58 coaxial cable with BNC connector.
10 Base T-
In 10 Base T network type allow stations to be attach via twisted pair cable. In 10 Base T the “10” refers to the transmission speed 10 Mbps and “T” refers to twisted pair cable. In a 10 Base T network each computer (node) is connected to a HUB.
10 Base F-
In the 10 Base F network uses the Fiber Optic cable for setup the network. Possesses excellent immunity and is the method of choice when running between buildings or widely separated HUBs. 10 Base F is expensive as the connectors and terminators used in 10 Base F are costly.
Comparing Ethernet Types-
| Ethernet Type | 10 Base 5 | 10 Base 2 | 10 Base T | 10 Base F |
| Media Type | Thick Coaxial | Thin Coaxial | UTP | Fiber Optic |
| Maximum Segment | 500 | 185 | 100 | 1000 |
| Frequency | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Maximum node per segment | 100 | 30 | 1024 | 1024 K |
==============================*************==============================

Wow, this post has given me useful info and answered some of my questions. I hope to give something back and aid others like you helped me. Feel free to surf my website Webemail24 about Vapes.
pantun promosi unik dan lucu pantun promosi unik dan lucu pantun promosi
unik dan lucu
You need to take part in a contest for one of the
most useful blogs online. I will highly recommend this site!
partai togel partai togel partai togel partai togel
I am actually thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared
this impressive paragraph at at this time.
bos88 bos88 bos88
My programmer is trying to persuade me to
move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because
of the costs. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on a number of
websites for about a year and am worried about switching to another platform.
I have heard great things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress content into it?
Any help would be really appreciated!
tim nasional sepak bola india tim nasional sepak bola india tim nasional sepak bola
india
Hello, all is going nicely here and ofcourse every one is sharing facts, that’s truly fine,
keep up writing.
kilat77 kilat77 kilat77
I am extremely impressed with your writing skills and also with the layout
on your weblog. Is this a paid theme or did you modify
it yourself? Either way keep up the nice quality writing, it is rare to see a great blog like this
one nowadays.
What’s up, everything is going sound here and ofcourse every one is sharing information,
that’s in fact fine, keep up writing.
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Seldom do I encounter a
blog that’s both equally educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you have
hit the nail on the head. The problem is something too few men and women are speaking intelligently about.
I am very happy I stumbled across this during my search for something regarding this.
If you are going for best contents like I do, simply go to see this website daily as it presents feature contents, thanks
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished
to say that I’ve truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts.
In any case I will be subscribing to your feed and I hope
you write again soon!
certainly like your web-site but you have to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts.
A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to tell the truth then again I will certainly come again again.