Ethernet is most widely used network technology. The IEEE802.3 standard introduces the Ethernet network. Here we are going to know about 10 Base T and 10 Base FL Ethernet system. Some high speed Ethernet networks are-
- 100 Base Ethernet
- Gigabit Ethernet
- Switched Ethernet
- Full duplex Ethernet
Features Of Advanced Ethernet-
Advanced Ethernet would use a physical star to match the robustness of Token Ring. It would not use more expensive coaxial cables and adopt inexpensive UTP cabling. It would use same frame types and speed of the older Ethernets so that new Ethernet will be compatible with older one.
10 Base T-
10 Base T Ethernet standard known as twisted pair Ethernet. 10 Base T uses a Star Bus topology. Network devices are connected to a HUB using pair of twisted pair cables. In 10 Base T 10 refers to 10 Mbps transmission speed, Base is for baseband signaling and T stands for twisted pair cable.
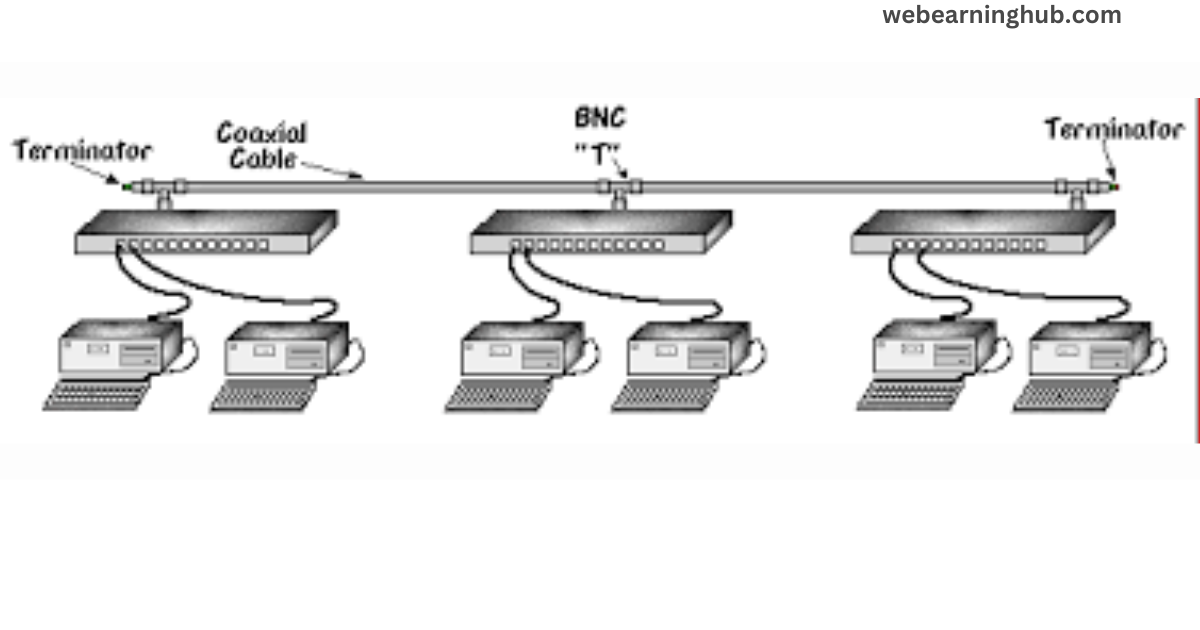
Features-
- Failure of one system dose not affect entire network
- Easy to troubleshoot
- Addition and removal of devices dose not affect network
- Fault tolerance
Limitations-
- Distance
- Sensitive to noise
- Limited numbers of computers can connected
10 Base T Topology-
It uses a physical Star topology in which each node connected to a central HUB. The HUB is a multi port repeater. It receives the signal from one port, regenerates it and passes the signal to all the other ports.
10 Base FL (Fiber Link)-
10 Base FL Ethernet standards that operates over fiber optic cable and covers a distance up to 2 K.M. In this network multimode fiber and Straight Tip (ST) connectors are used to build 10 Base FL segment.
10 Base FL Components
↓ ↓
Network Medium Medium Attachment Unit (MAU)
5-4-3 Role-
This role is to developed to limit the size of an Ethernet collision domain. This role is implemented by the Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) for number of repeaters and segments on shared access. The role states that : any two nodes in the network should be separated by more 5 segments, 4 repeaters and 3 populated segments.
High Speed Ethernet-
It is developed to increase connectivity speed between the terminals or computers in a network.
Ethernet Standards
↓ ↓ ↓
Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet 10 Gigabit Ethernet
100 Base Ethernet
100 Base Ethernet-
100 Base Ethernet supports data transfer rate up to 100 Mbps. It is also called as Fast Ethernet. CAT 5 and Fiber cables are used to build this network type.
Advantage-
- Speed is 10 times faster than regular 10 Base T network.
- Through put- Faster video, multimedia, graphics, internet surfing and other applications that are required high speed.
Disadvantage-
- Mode of data transfer- 100 Base T4 Ethernet cannot support full duplex mode of data transfer.
- Wiring- 100 Base T4 requires four pair of wiring for data transfer.
Gigabit Ethernet-
Gigabit Ethernet supports data transfer rate up to 1000 Mbps. This network is also called as 1000 Base T Ethernet.
Gigabit Ethernet Standards
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
1000 Base SX 1000 Base LX 1000 Base CX 1000 Base T 1000 Base TX
It was developed by IEEE 802.3ae in the year 2002. It supports data transfer rate is ten times faster than Gigabit Ethernet. This network is compatible with Synchronous Optical Network (SONET). This network supports segment length up to 40 K.M.s. This network uses full duplex mode of transmission and mostly run on fiber. This network includes standards as follows-
- 10 GBase – CX4
- 10 GBase – T
- 10 GBase – SR (Short Range)
- 10 GBase – LRM (Long Reach Multimedia)
- 10 GBase – LR (Long Range)
- 10 GBase – ER (Extended Range)
- 10 GBase – LX4
Switching Ethernet-
This Ethernet network employs a switch instead of a repeater or an Ethernet hub to connect individual hosts or segments. There are three types of switching-
- Cut through switching
- Store and forward switching
- Fragment free switching
Basic structure of switched Ethernet-

==============================*************==============================

1 thought on “Ethernet Advanced”